CDVAE: Cross Domain Variational Auto Encoder
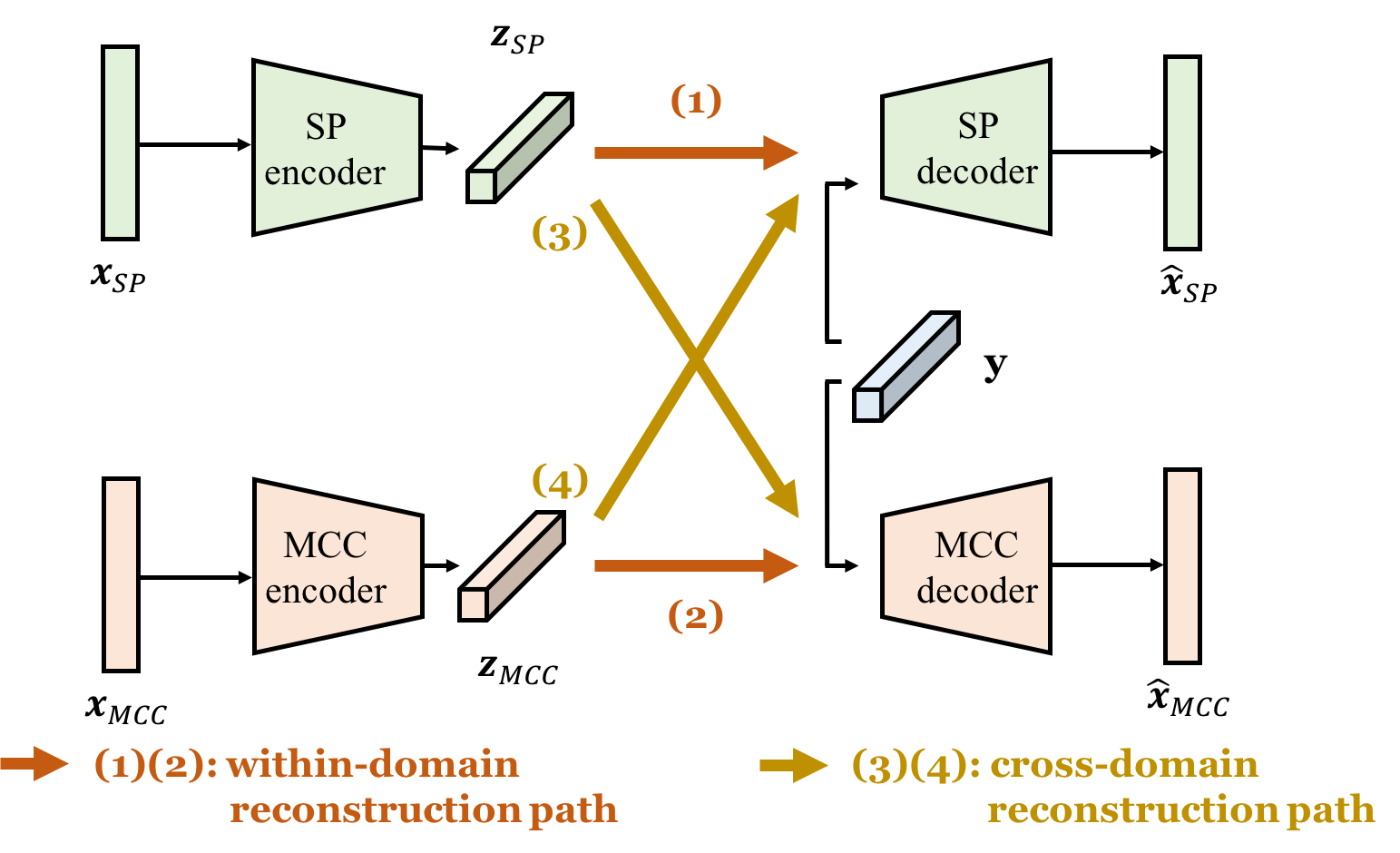
Demo page for paper: Voice Conversion Based on Cross-Domain Features Using Variational Auto Encoders
Paper
Wen-Chin Huang, Hsin-Te Hwang, Yu-Huai Peng, Yu Tsao, Hsin-Min Wang, Voice Conversion Based on Cross-Domain Features Using Variational Auto Encoders, ISCSLP 2018
CDVAE
An effective approach to non-parallel voice conversion (VC) is to utilize deep neural networks (DNNs), specifically variational auto encoders (VAEs), to model the latent structure of speech in an unsupervised manner. A previous study has confirmed the effectiveness of VAE using the STRAIGHT spectra for VC. However, VAE using other types of spectral features such as mel-cepstral coefficients (MCCs), which are related to human perception and have been widely used in VC, have not been properly investigated. Instead of using one specific type of spectral feature, it is expected that VAE may benefit from using multiple types of spectral features simultaneously, thereby improving the capability of VAE for VC.
We propose a novel VAE framework (called cross-domain VAE, CDVAE) for VC. Specifically, the proposed framework utilizes both STRAIGHT spectra and MCCs by explicitly regularizing multiple objectives in order to constrain the behavior of the learned encoder and decoder.
Subjective Evaluation Results
We evaluated our proposed framework on the Voice Conversion Challenge 2018 (VCC 2018) dataset. [Paper][Dataset]
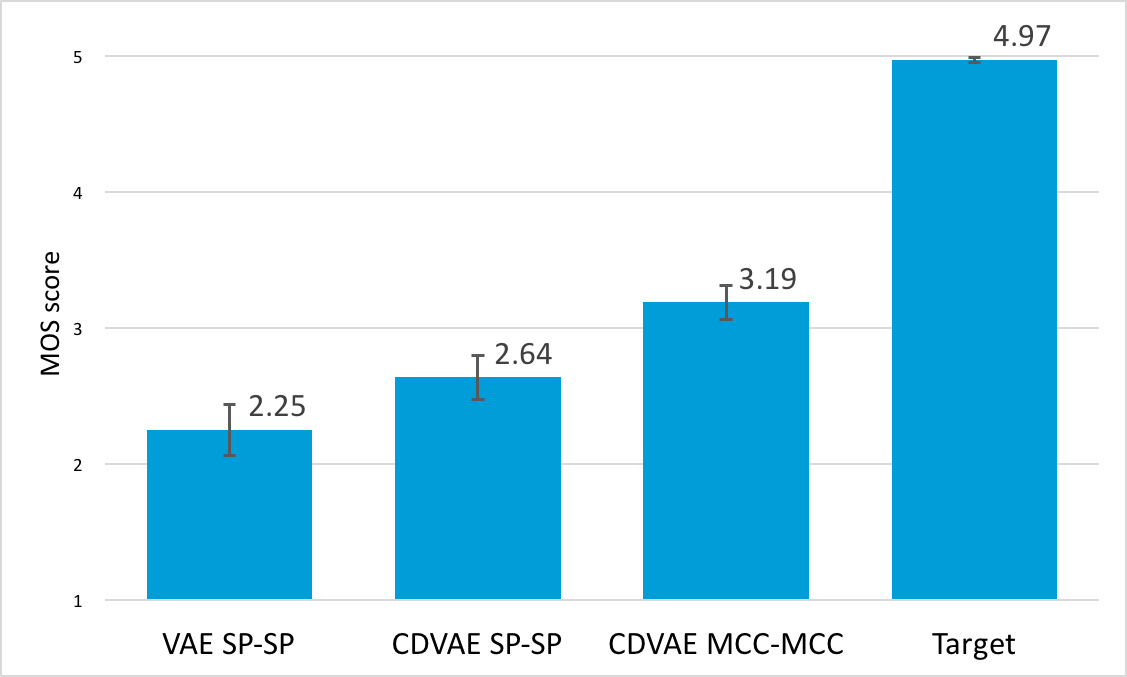
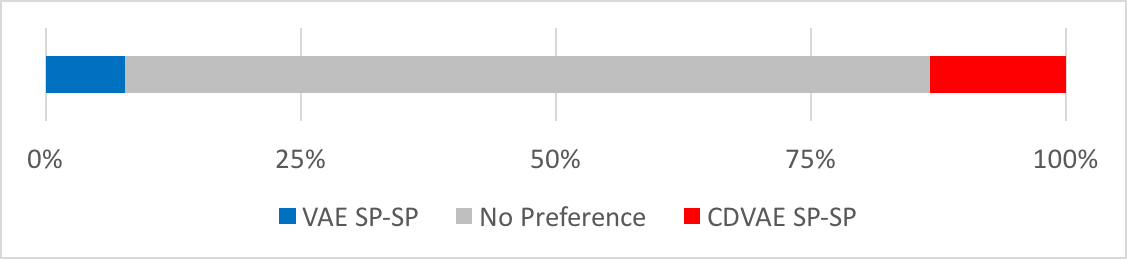
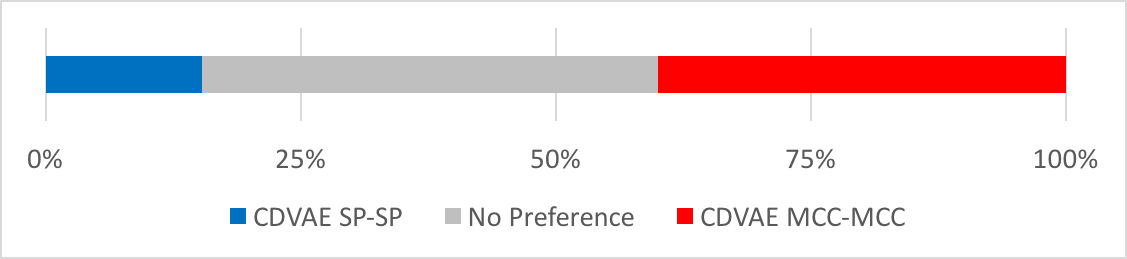
Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed CDVAE framework outperforms the conventional VAE framework in terms of subjective tests.
MOS on naturalness
Preference on Similarity
Speech Samples
The baseline model is VAE-VC, whose source code can be found here.
SF1-TF1
| Type | Sample |
|---|---|
| Source | |
| Target | |
| VAE SP-SP | |
| CDVAE SP-SP | |
| CDVAE MCC-MCC |
SF1-TM1
| Type | Sample |
|---|---|
| Source | |
| Target | |
| VAE SP-SP | |
| CDVAE SP-SP | |
| CDVAE MCC-MCC |
SM1-TF1
| Type | Sample |
|---|---|
| Source | |
| Target | |
| VAE SP-SP | |
| CDVAE SP-SP | |
| CDVAE MCC-MCC |
SM1-TM1
| Type | Sample |
|---|---|
| Source | |
| Target | |
| VAE SP-SP | |
| CDVAE SP-SP | |
| CDVAE MCC-MCC |